A high percentage of the population suffers from excruciating tooth pain, which is a common health issue that affects people as well as the community. It is defined as a severe, ongoing pain that comes from the teeth and surrounding tissues as a result of dental illness or damage. The key issue is, “What can you do to find relief?” despite whether you’re suffering from this degree of dental pain as a result of tooth decay, a dental injury, or an underlying problem. We will explore into unbearable tooth pain in this article.
What Is “Unbearable Tooth Pain”?
It might manifest as ranging from a persistent dull aching to sudden, intense flare-ups of pain. Additionally, a variety of conditions, such as gum disease, oral trauma, tooth decay, and even stress-induced teeth grinding, can cause it.

Unbearable Wisdom Tooth Pain?
At some point in their lives, many people battle with the terrible enemy of unbearable wisdom teeth pain. These problematic molars, which are frequently the last ones to pop out in a person’s late teens or early twenties, may seriously interfere with everyday living and cause severe discomfort that is almost unbearable. Because of the pain’s extreme severity and enduring nature, patients seek alleviation and understanding of the cause of their suffering. Impacted wisdom tooth pain is frequently linked to pericoronitis, an infection and inflammation of the soft tissues surrounding a partially erupted tooth. Dental caries, resorption of the next tooth’s roots, and, infrequently, tumors and cyst formation are further related conditions.
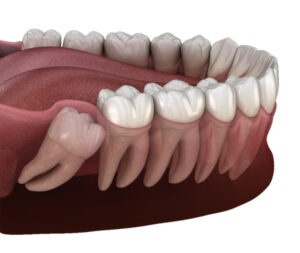
How Do I Make a Diagnosis for Wisdom Tooth Pain?
It’s best to consult your dentist if you have concerns about your wisdom teeth. Before examining your jaw and mouth, he or she will ask you about your symptoms. To determine the wisdom teeth’s position, an x-ray is taken. This comprehensive examination can help determine whether the wisdom teeth will emerge regularly or cause issues.
Why Do Wisdom Teeth Come and Go?
Many factors, including inflammation, impaction, infection, or tooth shifting, can cause intermittent wisdom tooth pain. For a precise evaluation and course of treatment that will minimize pain and avoid any more issues, it is crucial to see a dentist.
Treatment of Wisdom Tooth Pain
It is typically necessary to have one or more wisdom teeth extracted if they begin to cause troubles. Usually, this can be completed with a local anesthetic in an outpatient setting, that is, without requiring a hospital stay.
In the past, most people had their wisdom teeth extracted, even if they weren’t causing any issues. Nowadays, professionals typically only advise this if the teeth are troublesome or are predicted to become so in the future.
What Kills Tooth Pain Instantly?
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) are the preferred therapy for unbearable tooth pain because they suppress cyclooxygenase enzymes, which results in analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. Since ibuprofen and paracetamol perform better together than they do separately, taking them together has been recommended. Paracetamol or a mixture of paracetamol and oxycodone may be suggested if NSAIDs are contraindicated. opiates are only recommended as a supplement to ibuprofen or paracetamol at the lowest dose and for the shortest amount of time because they provide less analgesia and greater side effects. For relieving severe pain, especially in an emergency room, a dental block may be used as a first line of treatment before oral analgesics are administered.

How to Treat Swollen Gums Near Wisdom Tooth?
Acute pericoronitis (swollen & inflamed gum) often occurs as a single, brief episode that lasts three to four days and is accompanied by a typical eruption. The symptoms can be alleviated by improving local oral hygiene through the use of mouthwash containing chlorhexidine, dental cleaning, or brushing their teeth with toothpaste. To reduce the pain, a doctor may give ibuprofen or paracetamol. It is always best to take painkillers. Analgesic medications should never be placed alongside pericoronitis; this is a quite common, often ignorant patient error. Consult a dentist if the discomfort worsens or lasts longer than three to four days. It is advised to get the tooth extracted if the symptoms persist.
How to Stop Tooth Pain Fast at Home at Night?
Over-the-Counter Pain Relief Products
What to Use: Acetaminophen (Tylenol), aspirin, or ibuprofen (Advil) can all help lower inflammation and pain.
Dosage: For an appropriate dosage, refer to the label’s directions. Don’t take more than is advised.
The Cold Compressor
How to Use: Apply a cold compress or an ice pack to the exterior of your cheek in close proximity of the sore area.
Effect: The cold minimizes swelling and numbness discomfort. Apply for 15 to 20 minutes at a period, taking short breaks.
Rinse with Salt Water
How to Use It: In a glass of warm water, dissolve a teaspoon of salt. After about 30 seconds of swirling the solution around your mouth, spit it out.
Effect: Salt water assists in wound cleansing, inflammation decreasing, and healing.
Clove Oil

How to Use: Place a cotton ball containing a tiny bit of clove oil on the afflicted tooth. As an alternative, apply a few drops of clove oil mixed with a carrier oil like olive oil to the area that hurts.
Effect: Eugenol, a naturally occurring analgesic and antibacterial ingredient found in clove oil, can help alleviate pain and lessen infection.
Garlic
How to Use: Apply a paste made from crushed bulbs of garlic to the affected area. Another option is to slowly chew a garlic bulb.
Effect: Due to its antibacterial effects, garlic assists in reducing infection and relieve discomfort.
Summary
Physicians who are knowledgeable about common dental conditions may manage tooth pain. While antibiotics are utilized as an adjuvant when there is systemic involvement, infection spread, or immunocompromised people, analgesics such as paracetamol and ibuprofen work well together.
References
- Timmerman, A., & Parashos, P. (2020). Management of dental pain in primary care. Australian prescriber, 43(2), 39–44. https://doi.org/10.18773/austprescr.2020.010.
- Renton, T., & Wilson, N. H. (2016). Problems with erupting wisdom teeth: signs, symptoms, and management. The British journal of general practice: the journal of the Royal College of General Practitioners, 66(649), e606–e608. https://doi.org/10.3399/bjgp16X686509.
- Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG). (2023, September 5). Overview: Wisdom teeth. In InformedHealth.org [Internet]. Cologne, Germany. National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279591/.
- Cohen, L. A., Bonito, A. J., Akin, D. R., Manski, R. J., Macek, M. D., Edwards, R. R., & Cornelius, L. J. (2009). Toothache pain: behavioral impact and self-care strategies. Special care in dentistry: official publication of the American Association of Hospital Dentists, the Academy of Dentistry for the Handicapped, and the American Society for Geriatric Dentistry, 29(2), 85–95. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1754-4505.2008.00068.x