Introduction
Bleeding stomach ulcer is a serious medical issue that can lead to significant health risks if left untreated.
These signs can vary from mild pain to life-threatening complications.
Recognizing bleeding stomach ulcer symptoms can make a critical difference in receiving timely treatment.
Proceed with the article for a thorough explanation of the most common signs, underlying causes, and when to seek immediate medical attention.
Bleeding Ulcer Causes
A bleeding stomach ulcer is an open sore developed when stomach acid exposes underlying blood vessels
In contrast, another type of ulcer is called duodenal ulcer forms at the beginning of the small intestine.
Bleeding stomach ulcer symptoms occur when stomach acid damages the protective lining, often due to several risk factors contribute to bleeding ulcers, these factors may include:
- Infection with helicobacter pylori.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications
- Other risk factors.
Infection With Helicobacter Pylori
Helicobacter pylori, commonly known as a gram-negative bacillus H.pylori that lives within stomach epithelial cells.
It possesses flagella, which enables its movement toward the gastric mucosal layer.
This mobility aids in the bacteria’s ability to colonize and invade the stomach lining, potentially leading to ulcers. If left untreated, these ulcers can progress to bleeding ulcers.
According to research, approximately two-thirds of the global population is infected with H. pylori.
Thus, the bacteria primarily spread from person to person through contaminated food or water, as well as exposure to infected stool, vomit, or saliva.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) like aspirin and ibuprofen are used to treat fever, pain, and inflammation.
However, they are considered the second most significant risk factor for developing bleeding ulcers in the stomach or duodenum, after Helicobacter pylori infection.
NSAIDs promote the formation of bleeding stomach ulcers by suppressing the enzymes COX-1 and COX-2 in the gastrointestinal system.
As a result, the production of prostaglandins, which are substances with cytoprotective properties for the stomach mucosal layer, is inhibited.
Therefore, bleeding and mucosal injury are elevated as a result of the reduction in prostaglandin levels.
Furthermore, certain variables can increase your chance of having bleeding stomach ulcers while taking NSAIDs. This includes:
- Taking excessive doses of NSAIDs.
- An infection with H. pylori.
- Taking low-dose aspirin every day.
- Other medications interfere with NSAIDs, causing ulcers.
Other risk factors
Furthermore, there are several lower-risk variables that cause ulcers, including:
- Infection with pathogens rather than H. pylori, such as viruses or bacteria.
- Surgery that may affect the stomach or duodenum.
- Diseases like cirrhosis, cancer, and Crohn’s disease.
- A tumor called gastrinoma produces an abnormal amount of stomach acid.
Bleeding Stomach Ulcer Symptoms
There are common signs of stomach ulcers include:
- Upper abdominal pain.
- Vomiting and nausea.
- Burping: the process of releasing gas from the stomach through the mouth.
- Becoming full during or after eating.
- Heartburn.
If the prior symptoms are left untreated, internal bleeding of the stomach ulcer begins, resulting in bleeding stomach ulcer symptoms.
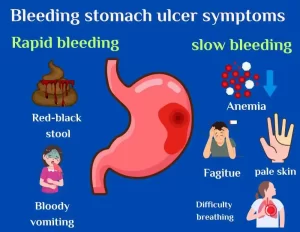
The following symptoms may vary depending on how the bleeding seems:
- Slow and continual bleeding causes anemia and contributes to symptoms such as tiredness, pale looks, and difficult breathing.
- Rapid and severe bleeding results in dark or red-black feces and bloody vomiting.
Bleeding Stomach Ulcer Treatment
Your doctor will begin making a treatment strategy for your stomach ulcer based on its etiology.
Health care provider suggests course of antibiotics and proton pump inhibitor drugs that reduce stomach acid to heal ulcers if you have stomach ulcers caused by H.pylori infection alone, NSAID use, or both.
Your doctor may recommend the following if you have bleeding stomach ulcer symptoms:
- Perform a gastroscopy to determine the cause of bleeding, and it can use to halt bleeding.
- Doctor requires surgery to repair the damaged blood vessels.
- Blood transfusions are recommended to replenish missing blood.
Bleeding Duodenal Ulcer Symptoms
An additional form of peptic ulcer is a duodenal ulcer, which can also induce symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and unexplained weight loss.
However, Patients with melena, hematemesis and anemia are suffering from bleeding duodenal ulcers.
Bleeding Duodenal Ulcer Treatment
Endoscopy is the first-line process for diagnosing and treating and identifying the location of bleeding duodenal ulcer.
The gastrointestinal endoscopy typically involves injection of vasoconstrictors and/or the use of clips.
If the endoscopy treatment fails, the doctor recommends surgery depending on ulcer suture with or without double ligation of the gastroduodenal artery or distal gastrectomy with partial duodenectomy.
Can You Die From a Bleeding Ulcer
A rare consequence known as perforation happens when the stomach lining splits and opens into the abdominal cavity.
This can lead to peritonitis, a disorder where stomach bacteria infiltrate the blood-formed sepsis and subsequently go to other organs, ultimately resulting in their failure.
If treatment is not received right away, this results in death.
Summary
Bleeding stomach ulcers are serious medical issues that can lead to significant health risks if left untreated.
Helicobacter pylori and NSAIDs are both serious risk factors for stomach and duodenal bleeding ulcers.
Bleeding stomach ulcer symptoms can vary depending on the bleeding appearance, from slow to severe bleeding causing anemia, dark or red-black feces, and bloody vomiting.
Proton pump inhibitors and antibiotics used to treat bleeding stomach ulcers.
While bleeding duodenal ulcers involves endoscopy, surgery may be recommended.
Bleeding ulcers can cause a rare complication called peritonitis that leads to death if left untreated.
References
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (n.d.). Symptoms & causes of peptic ulcers (stomach or duodenal ulcers) – NIDDK. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. From NIH
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (n.d.-b). Treatment for peptic ulcers (stomach or duodenal ulcers) – NIDDK. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. From NIH
- NHS. (n.d.). NHS choices.From NHS
- Drini, M. (2017, June). Peptic ulcer disease and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Australian prescriber. From PubMed
- (PDF) peptic ulcer disease – researchgate. (n.d.). From Researchgate
- Quinones, G. A. O. (2023, April 17). Duodenal ulcer. StatPearls [Internet]. From NIH
- Loffroy, R. (2013, February 21). Management of duodenal ulcer bleeding resistant to endoscopy: Surgery is dead!. World journal of gastroenterology. From PubMed
- Darmon, I., Rebibo, L., Diouf, M., Chivot, C., Riault, C., Yzet, T., Mouel, J. P. L., & Regimbeau, J.-M. (2020, April 3). Management of bleeding peptic duodenal ulcer refractory to endoscopic treatment: Surgery or transcatheter arterial embolization as first-line therapy? A retrospective single-center study and systematic review – european journal of trauma and emergency surgery. SpringerLink.From link springer