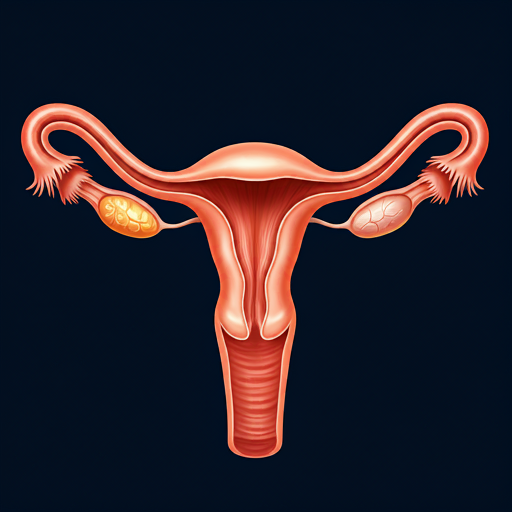
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that affects the cells in the cervix.
Most of these cases are caused by infection with the human papillomavirus.
Preventing this disease requires practicing safe sex and performing periodic examinations to ensure that the body is safe from the disease.
Stage 1 cervical cancer symptoms may include; vaginal bleeding or watery or bloody vaginal discharge and pelvic pain.
Cervical cancer doesn’t cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages.
Types of cervical cancer
There are two main types of cervical cancer:
- Squamous cell carcinoma: which accounts for about 80% – 90% of cervical cancer cases.
- Adenocarcinoma: It represents 10% – 20% of cases of the disease.
Sometimes women suffer from a mixture of both types.
Causes of cervical cancer
Most cases of cervical cancer are caused by infection with human papillomavirus, a sexually transmitted infection.
A large percentage of people are infected with HPV at some point in their lives and do not realize it because their bodies fight the infection.
But if your body doesn’t fight the infection, it may cause cervical cells to turn into cancer cells.
Human papillomavirus and cervical cancer
There are more than 100 types of HPV, of which ten can lead to cancer.
Early detection of HPV strains is essential in preventing cervical cancer.
Vaccination against HPV helps you prevent the disease in 90% of cases in which the virus is responsible for the disease.
Early Warning Signs of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer usually causes no symptoms in its early stages.
Hence the necessity of conducting periodic examinations, as early detection of cervical cancer can achieve many benefits by increasing the chances of recovery from the disease.
As the condition progresses, some initial symptoms may appear, such as:
Vaginal bleeding: which can occur after sex, between periods, or after menopause, or cause the menstrual period to be longer or heavier than usual.
Vaginal discharge: These secretions may be watery or bloody, and may also be accompanied by a foul odor.
Pelvic pain: It may be continuous or occur during intercourse.
The spread of the disease can cause the following symptoms:
- Difficulty urinating.
- Pain when urinating.
- The presence of blood in the urine.
- diarrhea.
- Pain or bleeding from the rectum when defecating.
- Fatigue.
- Weight loss
- Anorexia.
- A general feeling of illness.
- Mild back pain
- Swelling in the legs.
- Pelvic pain.
- Abdominal pain.
Therefore, if you suffer from these symptoms or some of them, you should seek medical care and perform the necessary tests to ensure your safety and receive appropriate treatment. ( Zhang, Xu , Zhang, & Qiao , 2020)
Changes in Menstrual Patterns
It is possible that some changes in menstrual patterns may occur and this does not mean that you suffer from cervical cancer.
As for the changes associated with the disease, they include abnormal bleeding that can appear in one of the following forms:
- Bleeding between menstrual periods.
- Bleeding after intercourse.
- Long duration of bleeding during menstruation.
- Heavy blood flow during menstruation.
- Postmenopausal bleeding.
We must keep in mind that such symptoms may have many causes other than cervical cancer.
Therefore, if you suffer from these symptoms, consult your doctor and do the necessary tests.
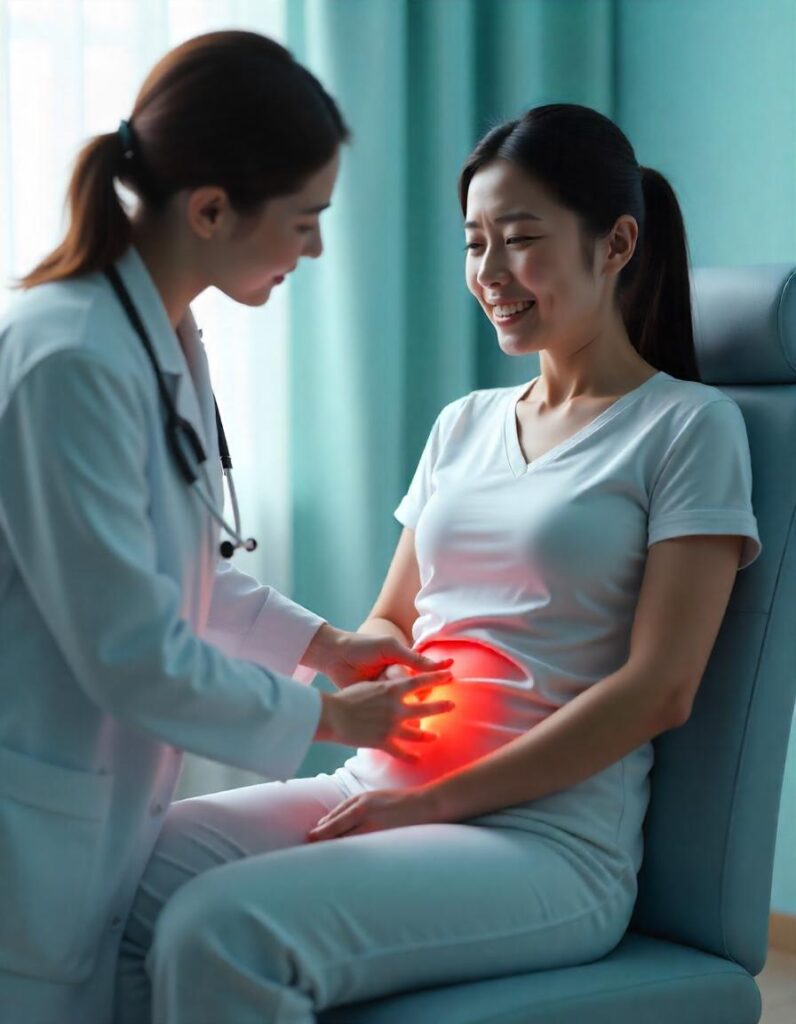
Pelvic Pain and Discomfort Explained
Pelvic pain usually does not appear as one of the stage 1 cervical cancer symptoms, but as the disease progresses, these symptoms can appear as a result of:
- The spread of cancer cells to the tissues surrounding the cervix in the pelvic area.
- Pressure on the nerves in the pelvic area as a result of the spread of the disease.
- Inflammation is also one of the factors that can cause pain and discomfort in the pelvic area, which arises as a result of the spread of diseased cells.
Note: Pelvic pain can have many other causes, so you should get the necessary tests if you suffer from these symptoms.
Read Also: How to Check for Ovarian Cancer at Home
When Spotting May Indicate Cancer
Spotting can be a sign of many health problems, including cervical cancer.
If you experience any of these symptoms, you should seek health care to confirm the real cause of the problem:
- Bleeding after menopause: is abnormal and usually indicates the presence of cancer such as cervical cancer or endometrial cancer.
- Bleeding between two periods: may indicate endometrial cancer, cervical cancer, or other types of diseases.
- Bleeding after intercourse: can indicate the presence of cervical cancer, and it can also be a sign of infections or benign tumors.
- Blood spots accompanied by pain: It can also be a sign of serious diseases, including cancer.
Note: Blood spots can be caused by non-cancerous conditions such as hormonal imbalance, uterine fibroids, or infections.
In all cases, it is preferable to consult a doctor to determine the cause of the spots and rule out any potential concerns.
Screening Methods for Early Detection
There are two main ways to detect the presence of cervical cancer:
- Pap test (Pap smear): Cells are collected from the cervix and examined to ensure that there are no abnormal cells that indicate the possibility of cancer.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) test: during which the presence of dangerous types of the virus that can cause cervical cancer is confirmed.
It is recommended to conduct periodic examinations for the disease as follows:
- Ages 21-29: Pap test every 3 years.
- Ages 30 to 65: HPV testing every 5 years, or a combination of HPV testing and Pap testing every 5 years.
Stages of cervical cancer
There are four stages of cervical cancer that can be described as follows:
Stage I: Cancer cells are found only in the cervix without spreading to other areas of the body.
Stage II: Cancer cells spread to other areas, such as the lower part of the vagina or the lining of the area inside the hips, but do not reach the pelvic wall.
Stage III: The disease spreads to the vagina, ureters, and nearby lymph nodes and may reach the pelvic wall.
Stage IV: The disease can spread to the lungs, bones, bladder, or other organs of the body.
Cervical Cancer Treatment
Cervical cancer treatment options may include: chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and surgery.
The specific treatment plan is tailored to the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and their future fertility goals.
In addition to traditional medical treatments, some patients may explore complementary therapies such as herbal treatments, acupuncture, or dietary changes.
However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure these therapies are safe and appropriate, and to coordinate them with the primary treatment plan. ( Wipperman , Neil, & Williams , 2018)
We hope that you have obtained all the information you need regarding the stage 1 cervical cancer symptoms through the article.
Read Also: Symptoms of Lung Cancer in Females
References
Wipperman , J., Neil, T., & Williams , T. (2018). Cervical Cancer: Evaluation and Management . PubMed.
Zhang, S., Xu , H., Zhang, L., & Qiao , Y. (2020). Cervical cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors and screening . PubMed.